数据集标签文件格式转换
本周主要进行了coco2017数据集的训练,同时学习了一些理论知识。关于coco数据集我在此提供一些使用用法,并且补充常用的标签文件之间的相互转换的Python代码。
COCO格式(.json)转换为YOLO格式(.txt)
首先要先下载好coco2017的完整数据集,其中包括训练集、验证集和测试集,20G左右,其中Annotations文件夹里的instances_train2017.json和instances_val2017.json这两个文件就是我们要转换的标签文件(.json)。
其次在你的项目根目录处创建目录,格式如下,其中images目录和labels目录一定要同级且一一对应。并且你的images和labels的数量也要对得上,不然后面训练不了!!!
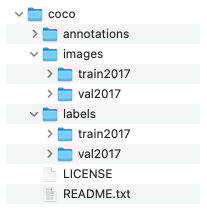
接下来重点就是怎么把COCO格式转换为YOLO格式了!
在你的根目录处创建一个.py后缀的新建文件,然后运行下面的代码就可以成功实现格式的转换了!
#COCO 格式的数据集转化为 YOLO 格式的数据集
#--json_path 输入的json文件路径
#--save_path 保存的文件夹名字,默认为当前目录下的labels。
import os
import json
from tqdm import tqdm
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
#这里根据自己的json文件位置,换成自己的就行
parser.add_argument('--json_path', default='D:/BaiduNetdiskDownload/COCO2017/annotations_train2017/annotations/instances_train2017.json',type=str, help="input: coco format(json)")
#这里设置.txt文件保存位置
parser.add_argument('--save_path', default='D:/BaiduNetdiskDownload/COCO2017/Lable/train2017', type=str, help="specify where to save the output dir of labels")
arg = parser.parse_args()
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1. / (size[0])
dh = 1. / (size[1])
x = box[0] + box[2] / 2.0
y = box[1] + box[3] / 2.0
w = box[2]
h = box[3]
#round函数确定(xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax)的小数位数
x = round(x * dw, 6)
w = round(w * dw, 6)
y = round(y * dh, 6)
h = round(h * dh, 6)
return (x, y, w, h)
if __name__ == '__main__':
json_file = arg.json_path # COCO Object Instance 类型的标注
ana_txt_save_path = arg.save_path # 保存的路径
data = json.load(open(json_file, 'r'))
if not os.path.exists(ana_txt_save_path):
os.makedirs(ana_txt_save_path)
id_map = {} # coco数据集的id不连续!重新映射一下再输出!
with open(os.path.join(ana_txt_save_path, 'classes.txt'), 'w') as f:
# 写入classes.txt
for i, category in enumerate(data['categories']):
f.write(f"{category['name']}\n")
id_map[category['id']] = i
# print(id_map)
#这里需要根据自己的需要,更改写入图像相对路径的文件位置。
list_file = open(os.path.join(ana_txt_save_path, 'train2017.txt'), 'w')
for img in tqdm(data['images']):
filename = img["file_name"]
img_width = img["width"]
img_height = img["height"]
img_id = img["id"]
head, tail = os.path.splitext(filename)
ana_txt_name = head + ".txt" # 对应的txt名字,与jpg一致
f_txt = open(os.path.join(ana_txt_save_path, ana_txt_name), 'w')
for ann in data['annotations']:
if ann['image_id'] == img_id:
box = convert((img_width, img_height), ann["bbox"])
f_txt.write("%s %s %s %s %s\n" % (id_map[ann["category_id"]], box[0], box[1], box[2], box[3]))
f_txt.close()
#将图片的相对路径写入train2017或val2017的路径
list_file.write('./images/train2017/%s.jpg\n' %(head))
list_file.close()
代码中有注释以及你要结合自己文件名的实际情况需要进行修改的地方都标注好了。
可扩展标记语言格式(.xml)转换为YOLO格式(.txt)
首先要准备好你的已经打好标签的xml格式的标签文件,然后运行以下代码应该就可以了。
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import pickle
import os
from os import listdir, getcwd
from os.path import join
def convert(size, box):
# size=(width, height) b=(xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
# x_center = (xmax+xmin)/2 y_center = (ymax+ymin)/2
# x = x_center / width y = y_center / height
# w = (xmax-xmin) / width h = (ymax-ymin) / height
x_center = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0
y_center = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0
x = x_center / size[0]
y = y_center / size[1]
w = (box[1] - box[0]) / size[0]
h = (box[3] - box[2]) / size[1]
# print(x, y, w, h)
return (x, y, w, h)
def convert_annotation(xml_files_path, save_txt_files_path, classes):
xml_files = os.listdir(xml_files_path)
# print(xml_files)
for xml_name in xml_files:
# print(xml_name)
xml_file = os.path.join(xml_files_path, xml_name)
out_txt_path = os.path.join(save_txt_files_path, xml_name.split('.')[0] + '.txt')
out_txt_f = open(out_txt_path, 'w')
tree = ET.parse(xml_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
w = int(size.find('width').text)
h = int(size.find('height').text)
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
# if cls not in classes or int(difficult) == 1:
# continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
# b=(xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
# print(w, h, b)
bb = convert((w, h), b)
out_txt_f.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 把forklift_pallet的voc的xml标签文件转化为yolo的txt标签文件
# 1、需要转化的类别
classes = ['People', 'Car', 'Bus', 'Motorcycle', 'Lamp', 'Truck']
# 2、voc格式的xml标签文件路径
xml_files1 = r'D:\Technology\Python_File\yolov5\M3FD\Annotation_xml'
# xml_files1 = r'C:/Users/GuoQiang/Desktop/数据集/标签1'
# 3、转化为yolo格式的txt标签文件存储路径
save_txt_files1 = r'D:\Technology\Python_File\yolov5\M3FD\Annotation_txt'
convert_annotation(xml_files1, save_txt_files1, classes)主要要改的地方就是结尾处的3个注释处了,请你结合自己文件名的实际情况进行修改。
以上就是常用的标签文件格式的转换代码,由于主要面向YOLO格式(.txt),故我在这里也只提供其它常用标签文件格式转换为YOLO格式的代码,如果你需要其它格式的转换代码,请你自行上CSDN进行搜索即可解决问题。
数据集标签文件格式转换
http://localhost:8090//archives/ben-zhou-xiao-jie-ti-gong-shu-ju-ji-ge-shi-zhuan-huan-w